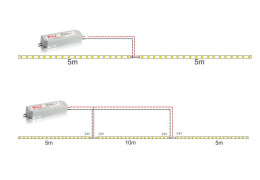
Avoid dim, uneven LED strips. Learn practical ways to prevent voltage drop on long runs: correct wiring, cable...
Search in blog
Blog categories
Blog tags
Photo gallery
-

LED Lighting Colour Temperature Comparison
-

Flexible LED Strip Lighting
-

Modern LED Lighting Ideas for Home Interiors












Latest comments